The Database for Agentic Workloads
Agents don’t query—they explore, branch, and multiply. TiDB unifies vectors, transactions, and analytics to handle this, letting you provision databases instantly, operate at scale, and keep costs under control.
Agents don’t query—they explore, branch, and multiply. TiDB unifies vectors, transactions, and analytics to handle this, letting you provision databases instantly, operate at scale, and keep costs under control.


Traditional databases were designed for predictable, human-driven workloads. Agentic systems operate fundamentally differently.
Agentic workloads don’t scale linearly; they multiply. This X tenents × Y agents × Z branches problem creates operational bottlenecks and cost explosions on traditional databases. When one agent action can trigger thousands of new instances, legacy architectures fall apart.
See how Manus 1.5 uses TiDB X to let agents ship full-stack apps at scale.
AI applications need vectors, transactions, and analytics — all at once, in real-time.
Stitching together databases creates a fragile stack with sync issues and operational drag.
TiDB unifies your entire AI data stack:
Dify consolidated hundreds of thousands of containers onto TiDB, cutting operational overhead by 90%.
Unpredictable AI usage can lead to runaway bills. Over-provisioning for peak loads is wasteful, and without granular visibility, you can’t track costs per-tenant or per-agent.
TiDB gives engineering teams fine-grained control over cost and scale:
Pricing designed for modern platforms.
Leading AI innovators are solving scaling challenges with TiDB.

“TiDB’s elastic architecture enabled us to migrate in two weeks, supporting users and massive ‘Context Engineering’ workloads for viral success.”

“We consolidated our entire AI backend into TiDB—letting our engineers focus on building agent features instead of managing database complexity.”

“TiDB’s unified architecture enabled AI agents to access complete, real-time user context for autonomous marketing decisions.”

“Unified HTAP + Vector engine enabled hybrid queries combining semantic understanding with SQL precision for real-time conversational analytics.”

“Real-time architecture enabled storing and aggregating survey data on the fly, eliminating processing overhead.”
Explore interactive demos, deploy complete applications in our sandbox labs, and discover what the community is building.
pip install pytidb

Each agent can create its own database branch to safely test prompts, workflows, or data changes—without affecting live traffic or other agents.
import fetch from "node-fetch";
const BASE = "https://serverless.tidbapi.com/v1beta1";
async function createBranch(clusterId, branchName, publicKey, privateKey) {
const res = await fetch(`${BASE}/clusters/${clusterId}/branches`, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
Authorization:
"Basic " + Buffer.from(`${publicKey}:${privateKey}`).toString("base64"),
},
body: JSON.stringify({ displayName: branchName }),
});
if (!res.ok) throw new Error(`Create branch failed: ${res.status}`);
const { branchId } = await res.json();
return branchId;
}
// Example usage
createBranch(
"1234567890",
"new-feature-branch",
process.env.TIDB_CLOUD_PUBLIC_KEY,
process.env.TIDB_CLOUD_PRIVATE_KEY
)
.then((id) => console.log("Branch created:", id))
.catch(console.error);

Create AI assistants that understand context and meaning, not just keywords, using vector embeddings and retrieval-augmented generation.
class Chunk(TableModel):
__tablename__ = "chunks"
id: int = Field(primary_key=True)
text: str = Field()
text_vec: list[float] = text_embed.VectorField(
source_field="text",
)
meta: dict = Field(sa_type=JSON)
table = db.create_table(schema=Chunk, if_exists="overwrite")
results = (
table.search(query_text)
.debug(True)
.filter({"meta.language": language})
.distance_threshold(distance_threshold)
.limit(query_limit)
.to_list()
)

Enable multimodal search experiences where users can find images using text descriptions or discover similar visual content effortlessly.
class Pet(TableModel):
__tablename__ = "pets"
id: int = Field(primary_key=True)
breed: str = Field()
image_uri: str = Field()
image_name: str = Field()
image_vec: Optional[List[float]] = embed_fn.VectorField(
distance_metric=DistanceMetric.L2,
source_field="image_uri",
source_type="image",
)
results = (
table.search(query="fluffy orange cat")
.distance_metric(DistanceMetric.L2)
.limit(limit)
.to_list()
)

Get the best of both worlds by merging traditional full-text search with modern vector similarity for comprehensive, accurate results.
# Define table schema
class Document(TableModel):
__tablename__ = "documents"
id: int = Field(primary_key=True)
text: str = FullTextField()
text_vec: list[float] = embed_fn.VectorField(
source_field="text",
)
meta: dict = Field(sa_type=JSON)
query = (
table.search(query_text, search_type="hybrid")
.distance_threshold(0.8)
.fusion(method="rrf")
.limit(limit)
)

Transform your text, images, and documents into searchable vectors without manual preprocessing or complex embedding pipeline setup.
# Define embedding function
embed_func = EmbeddingFunction(
model_name="tidbcloud_free/amazon/titan-embed-text-v2"
# No API key required for TiDB Cloud free models
)
class Chunk(TableModel):
__tablename__ = "chunks"
id: int = Field(primary_key=True)
text: str = Field(sa_type=TEXT)
text_vec: list[float] = embed_func.VectorField(source_field="text")
table = db.create_table(schema=Chunk, if_exists="overwrite")
# Insert sample data - embeddings generated automatically
table.bulk_insert([
Chunk(text="TiDB is a distributed database that supports OLTP, OLAP, HTAP and AI workloads."),
Chunk(text="PyTiDB is a Python library for developers to connect to TiDB."),
Chunk(text="LlamaIndex is a Python library for building AI-powered applications."),
])

Automatically embed product data and deliver personalized recommendations that update in real-time as your inventory changes, without complex pipelines.
class Product(TableModel):
__tablename__ = "products"
id: int = Field(primary_key=True)
name: str = Field(sa_type=TEXT)
description: str = Field(sa_type=TEXT)
description_vec: list[float] = embed_func.VectorField(
source_field="description"
)
category: str = Field(sa_type=TEXT)
price: float = Field()
table = db.create_table(schema=Product, if_exists="overwrite")
# App-1 is inserting strings and vectors are auto-generated in real-time
table.insert(Product(
name="Professional Basketball",
description="High-quality basketball for professional and amateur players",
category="Sports",
price=29.99
))
# App-2 is searching at once using semantic similarity with user preferences
recommendations = (
table.search(user_profile)
.distance_threshold(distance_threshold)
.limit(5)
.to_list()
)
Each agent can create its own database branch to safely test prompts, workflows, or data changes—without affecting live traffic or other agents.
import fetch from "node-fetch";
const BASE = "https://serverless.tidbapi.com/v1beta1";
async function createBranch(clusterId, branchName, publicKey, privateKey) {
const res = await fetch(`${BASE}/clusters/${clusterId}/branches`, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
Authorization:
"Basic " + Buffer.from(`${publicKey}:${privateKey}`).toString("base64"),
},
body: JSON.stringify({ displayName: branchName }),
});
if (!res.ok) throw new Error(`Create branch failed: ${res.status}`);
const { branchId } = await res.json();
return branchId;
}
// Example usage
createBranch(
"1234567890",
"new-feature-branch",
process.env.TIDB_CLOUD_PUBLIC_KEY,
process.env.TIDB_CLOUD_PRIVATE_KEY
)
.then((id) => console.log("Branch created:", id))
.catch(console.error);
Create AI assistants that understand context and meaning, not just keywords, using vector embeddings and retrieval-augmented generation.
class Chunk(TableModel):
__tablename__ = "chunks"
id: int = Field(primary_key=True)
text: str = Field()
text_vec: list[float] = text_embed.VectorField(
source_field="text",
)
meta: dict = Field(sa_type=JSON)
table = db.create_table(schema=Chunk, if_exists="overwrite")
results = (
table.search(query_text)
.debug(True)
.filter({"meta.language": language})
.distance_threshold(distance_threshold)
.limit(query_limit)
.to_list()
)
Enable multimodal search experiences where users can find images using text descriptions or discover similar visual content effortlessly.
class Pet(TableModel):
__tablename__ = "pets"
id: int = Field(primary_key=True)
breed: str = Field()
image_uri: str = Field()
image_name: str = Field()
image_vec: Optional[List[float]] = embed_fn.VectorField(
distance_metric=DistanceMetric.L2,
source_field="image_uri",
source_type="image",
)
results = (
table.search(query="fluffy orange cat")
.distance_metric(DistanceMetric.L2)
.limit(limit)
.to_list()
)
Get the best of both worlds by merging traditional full-text search with modern vector similarity for comprehensive, accurate results.
# Define table schema
class Document(TableModel):
__tablename__ = "documents"
id: int = Field(primary_key=True)
text: str = FullTextField()
text_vec: list[float] = embed_fn.VectorField(
source_field="text",
)
meta: dict = Field(sa_type=JSON)
query = (
table.search(query_text, search_type="hybrid")
.distance_threshold(0.8)
.fusion(method="rrf")
.limit(limit)
)
Transform your text, images, and documents into searchable vectors without manual preprocessing or complex embedding pipeline setup.
# Define embedding function
embed_func = EmbeddingFunction(
model_name="tidbcloud_free/amazon/titan-embed-text-v2"
# No API key required for TiDB Cloud free models
)
class Chunk(TableModel):
__tablename__ = "chunks"
id: int = Field(primary_key=True)
text: str = Field(sa_type=TEXT)
text_vec: list[float] = embed_func.VectorField(source_field="text")
table = db.create_table(schema=Chunk, if_exists="overwrite")
# Insert sample data - embeddings generated automatically
table.bulk_insert([
Chunk(text="TiDB is a distributed database that supports OLTP, OLAP, HTAP and AI workloads."),
Chunk(text="PyTiDB is a Python library for developers to connect to TiDB."),
Chunk(text="LlamaIndex is a Python library for building AI-powered applications."),
])
Automatically embed product data and deliver personalized recommendations that update in real-time as your inventory changes, without complex pipelines.
class Product(TableModel):
__tablename__ = "products"
id: int = Field(primary_key=True)
name: str = Field(sa_type=TEXT)
description: str = Field(sa_type=TEXT)
description_vec: list[float] = embed_func.VectorField(
source_field="description"
)
category: str = Field(sa_type=TEXT)
price: float = Field()
table = db.create_table(schema=Product, if_exists="overwrite")
# App-1 is inserting strings and vectors are auto-generated in real-time
table.insert(Product(
name="Professional Basketball",
description="High-quality basketball for professional and amateur players",
category="Sports",
price=29.99
))
# App-2 is searching at once using semantic similarity with user preferences
recommendations = (
table.search(user_profile)
.distance_threshold(distance_threshold)
.limit(5)
.to_list()
)
Discover amazing projects built by our community. From developer tools to production applications, see what’s possible with TiDB’s AI-powered capabilities.
Web App
AI-powered RAG for healthcare management. Uses TiDB to organize documents, create smart schedules, and power family health chat.
DevOps
Serverless incident response system using TiDB vector search to ingest logs, triage incidents, and generate explainable reports.
Web App
Event-driven agentic system that automates workflows by finding similar past cases with TiDB vector search and generating appeal letters.
Web App
Agentic customer support platform using a custom .NET SDK for TiDB Vector Search to power intelligent ticket routing and real-time chat.
Web App
AI clinical decision support that analyzes medical images and uses TiDB for vector similarity search on cases to provide diagnostic guidance.
Web App
HVAC monitoring system using TiDB vector search for real-time sensor data analysis and predictive maintenance.
Web App
AI life sim game teaching finance via TiDB Cloud for decision storage and behavioral insights.
AI Agent System
AI multi-agent trading platform using TiDB for sentiment analysis and market verification.
Web App
AI finance assistant using RAG and TiDB for receipt/transaction insights and records.
AI Agent System
Multi-step AI agent using TiDB vector DB for RAG-based web form automation and validation.
Developer Tool
Chrome extension detecting AI text with TiDB backend for logging and feedback analytics.
AI Agent System
AI decision engine simulating outcomes with TiDB for stateful agentic reasoning.
AI Agent System
AI journaling system using TiDB for semantic search and pattern detection in entries.
Developer Tool
Git-style AI memory layer on TiDB with vector/full-text search and branching.
AI Agent System
LogiFlow AI platform using TiDB for vector search in logistics automation.
Connect with developers building the future with TiDB.

GitHub stars

Community Members

Contributors

Projects
Get hands-on with TiDB through our curated sandbox projects. Deploy complete applications in minutes and explore AI-powered database capabilities.

Learn to build AI apps with vector embeddings, RAG, hybrid search, and GraphRAG using TiDB Cloud Starter in 60 minutes.

Build intelligent apps that retrieve information and translate natural language to SQL using OpenAI models and TiDB Cloud Starter.

Create advanced AI agents with graph-enhanced retrieval and tool calling capabilities using OpenAI and TiDB Cloud Starter integration.
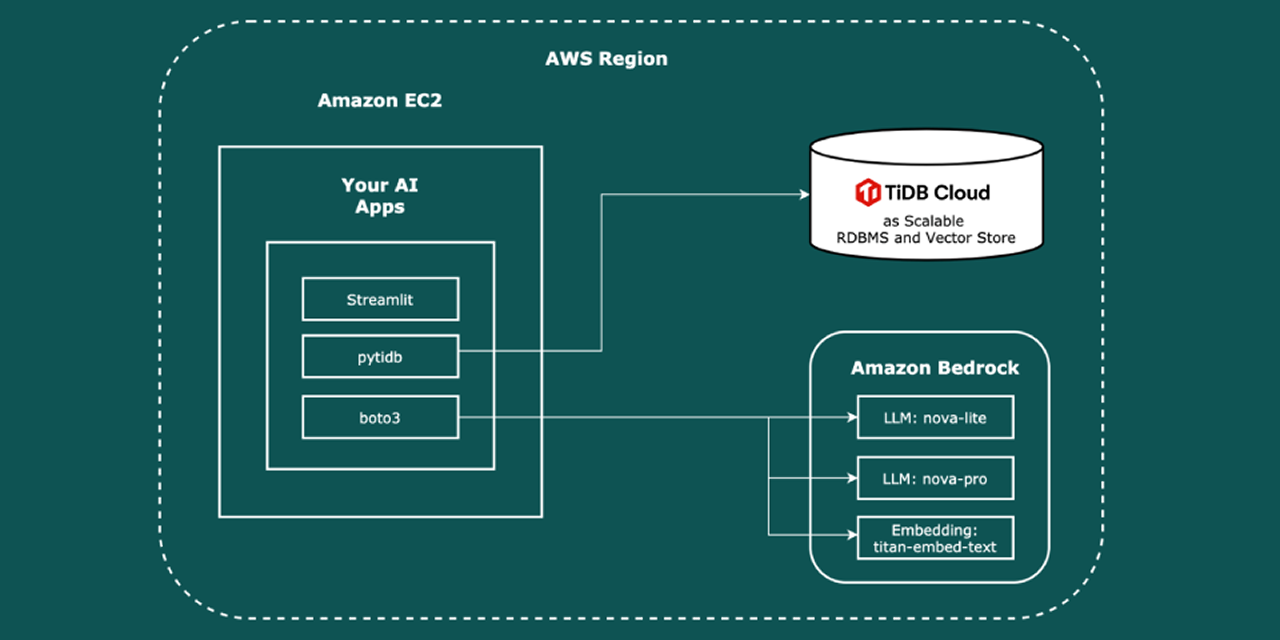
Develop AI applications with Amazon Bedrock models for retrieval-augmented generation and natural language query translation capabilities.
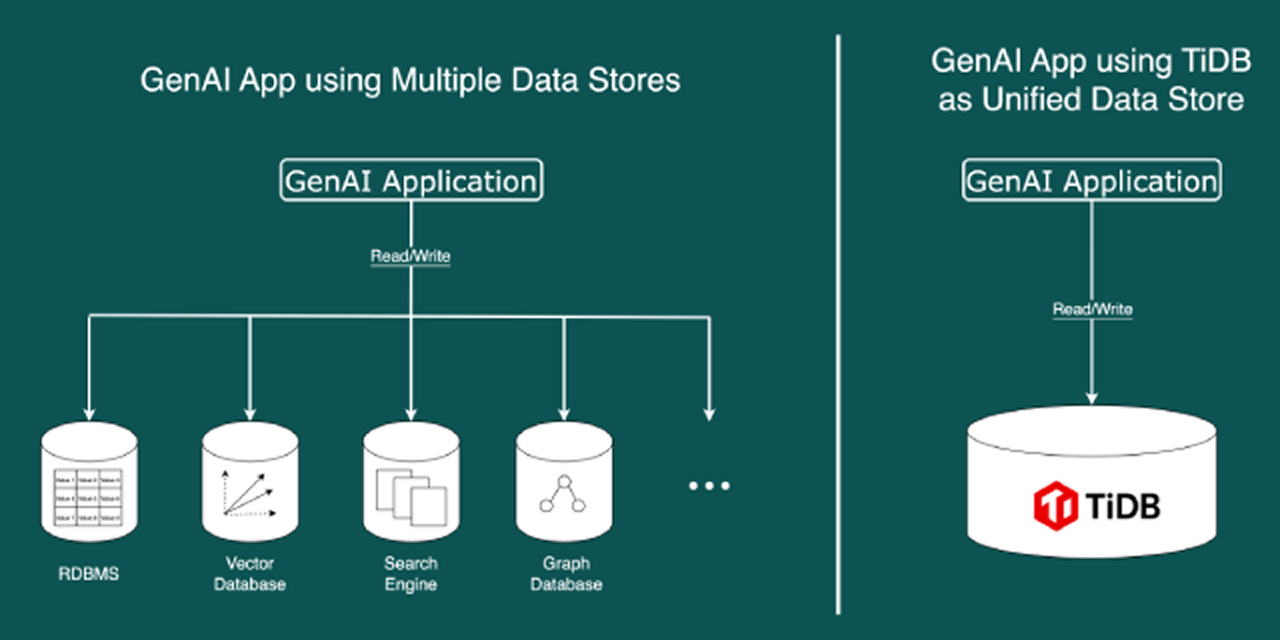
Experience the simplicity of using TiDB as single storage solution versus managing multiple databases for GenAI applications.

Compare multi-database complexity with TiDB’s unified approach for GenAI applications using OpenAI models and simplified development workflows.
Production-ready integrations for every stage of your AI pipeline.
Quick start: copy paste your Connection String into listed integrations.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()



Talk to Our AI Infrastructure Experts